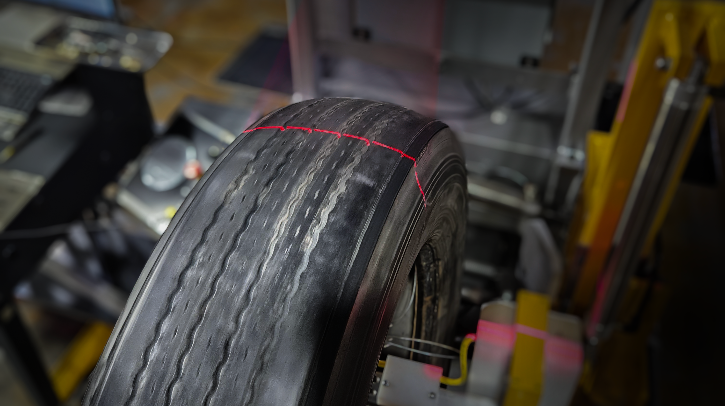
Michelin recently completed the rollout of its TreadEye system across its US retread network. TreadEye is a tread-depth and casing-condition measurement tool that records 1,200 measurement points per tire, offering fleets detailed insights into wear, damage and when a tire should be pulled. Scott Vanchoff, vice president of Michelin Retread Technologies, speaks with TTI about the technology, purpose and innovation behind the solution
What are the key technological advancements in TreadEye that differentiate it from traditional retread processes?
In a traditional retread process, the operator at the initial inspection post is tasked with manually measuring the tread depth of each tire that comes through their post. By automating the process to capture more than 1,200 points of measurement during initial inspection, any issues with accuracy or consistency associated with a manual process are eliminated.

How does TreadEye integrate with existing tire management systems and what data analytics capabilities does it offer to fleet operators?
TreadEye is incorporated into the initial inspection post/process. The data captured by TreadEye is available through the Fleet Business Insights platform. Having access to accurate, consistent tread depth data broken down by fleet terminal location gives fleet managers insight into their operations that wasn’t previously available.
For example, if their casing management procedures indicate tires should be pulled for retreading at 4/32nd and the data coming out of TreadEye shows that tires are consistently arriving at the plant for retreading at 7/32nds, the fleet may not be getting the full value out of their tire assets. On the flipside, if tires are consistently coming into the retread plant at 1/32nd, the fleet may be at risk for casing damage, DOT violations and additional downtime.
The tread depth data is reported by fleet terminal location, so the fleet manager can determine if they need to make adjustments to pull point procedures/training at specific locations or across the organization. The fleet manager is also able to associate reject rates and reasons with tread depth and potentially adjust their pull points to maximize tread life while protecting casings for future retreading.
What role do artificial intelligence and machine learning currently play – or could they play in the future – in optimizing the TreadEye retread process?
Michelin is reinventing the retread process through the incorporation of AI, robotics and advanced data analytics to deliver advancements in product quality and consistency, along with more efficient fleet operations. TreadEye is one part of the process. Future announcements will go into more detail on additional advancements we’re bringing to the retread process.
What are the environmental benefits of adopting TreadEye, particularly in terms of reducing the carbon footprint and promoting sustainability?
By closely managing pull points through the data made available through TreadEye, fleets are able to use their resources (the tire in this case) efficiently and reduce waste. They get more life out of their casings rather than disposing of them early due to casing damage, which can occur when tires are pulled too late, or buffing off good, usable tread rubber when pulling too early.
Explore: Ensuring quality in tire production with non-contact measurement solutions