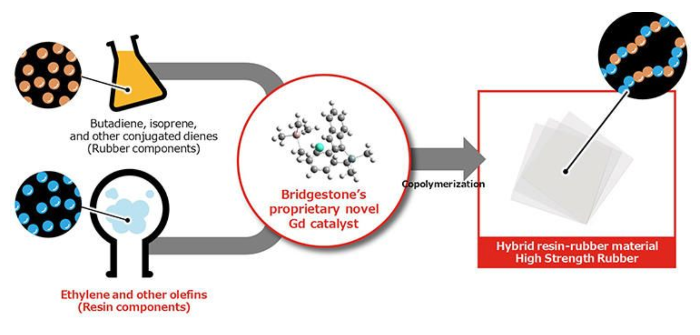
In its pursuit of more sustainable materials, Bridgestone has successfully developed what is claimed to be the world’s first polymer to bond rubber and resins at the molecular level.
This new polymer is extremely high durability, with crack resistance more than five times higher than natural rubber, abrasion resistance more than 2.5 times higher, and tensile strength more than 1.5 times higher than natural rubber, which itself has a greater destruction resistance than common synthetic rubber.
Badged High Strength Rubber (HSR), the hybrid material is used to bond synthetic rubber components, such as butadiene and isoprene, with resin components, such as ethylene, at the molecular level using Bridgestone’s proprietary novel gadolinium (Gd) catalyst (via copolymerization).
As a result, this next-generation material is able to combine the pliability of rubber with the toughness of resin. The breakthrough was achieved by further evolving the Gd catalyst technologies used to synthesize the polyisoprene rubber.
In future, HSR could be applied in tires that ultimately use fewer materials, but which still provide the desired performance levels.
The tire maker believes that the material will be essential in enabling it to achieve its 2050 goal of only using 100% sustainable materials in its products.